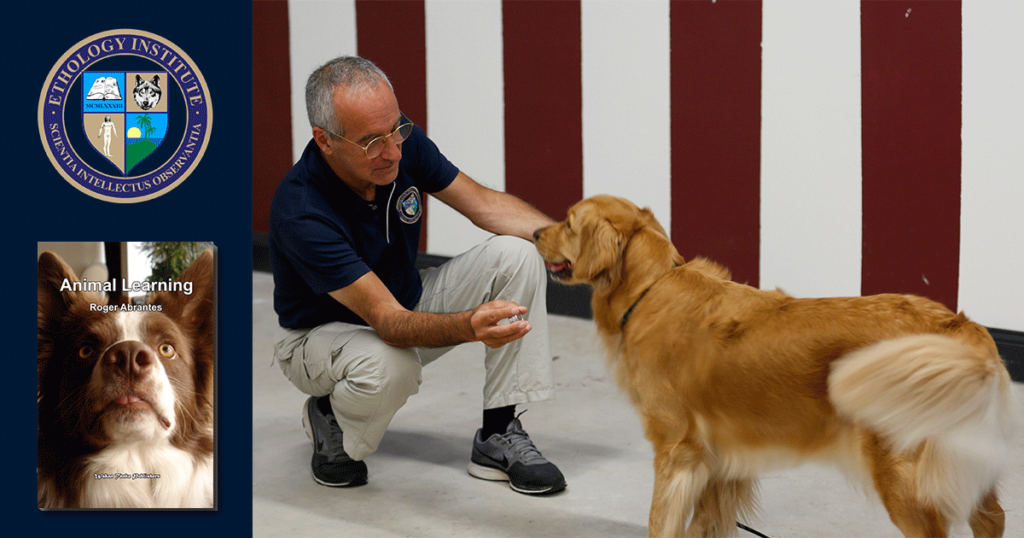
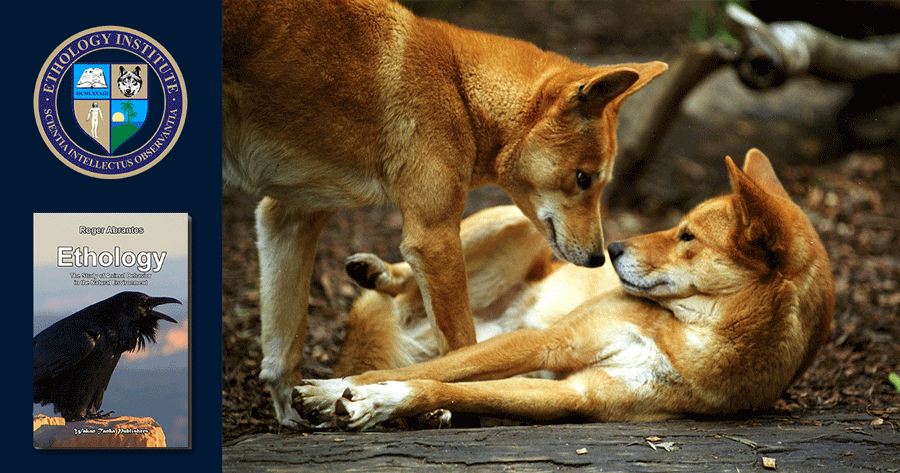
In the behavioral sciences, there is some confusion about the meaning of the terms signal and cue (as with so many other terms) and some authors use it interchangeably. To make it even more difficult, communication theory also uses the same terms with slightly different meanings and in the theatre and movies world a ‘cue’ is actually a ‘signal.’
However, in behavioral sciences, the general consensus (see references below) is that signal and cue have the following meanings.
A signal is a perceivable behavior or feature that has evolved and has acquired the specific characteristic of conveying information about the signaler or the signaler’s environment. Information (communication) changes the behavior or the beliefs of the receiver.
This definition of signal implies that if a signal changes the behavior of an organism, this change of behavior must be profitable to both sender and receiver more often than not, or otherwise, signalers would cease to send the signal and receivers would cease to respond. This definition distinguishes, in principle, a signal from coercion, although some signals may be coercive, e.g. threats.
In general, signals must be honest and reliable, or otherwise they cease to have any effect (receivers don’t behave appropriately) and they undermine communication (honest senders will not benefit from sending the signals). However, some signals can tolerate a certain degree of dishonesty, all depending on the costs and benefits for all parties. H. W. Bates discovered in 1861 that some (palatable) butterflies had an advantage in mimicking (Batesian mimicry) poisonous butterflies, which is detrimental to the poisonous butterflies inasmuch as it turns their signals of unpalatability less reliable. On the other side, some species use the same signals to convey the same information and they all benefit from it (Mullerian mimicry).
A cue is any feature that an organism can use as a guide to display a particular behavior or series of behaviors. The classical example is the mosquito seeking a mammal to bite and flying up wind when it detects CO2. The CO2 is a cue for the mosquito, but it is surely not a signal sent by the mammal, which would prefer to remain undetected and not be bitten. Intentionality is the key element to distinguish signals from cues.
A cue is a regularity, a pattern that either is permanently ‘on,’ or is ‘on’ and ‘off” depending on specific conditions, e.g. a rock, a tree, or the position of the sun in the sky cues us of directions, and dark clouds cues us of impending rain. The rock, the tree, the sun and the clouds are not there to give us information, but they do if we interpret them correctly. A signal is more malleable, more intentional and we can turn it ‘on’ and ‘off’ in response to relevant cues in the environment, e.g. the warning cry that many species (signal) issue in response to the appearance (cue) of a feared predator.
Cues are traits or actions that benefit the receiver exclusively. The sun and the rock do not profit from us getting our bearings. When a mouse by accident makes a rustling sound in the leaves and attracts a predator increasing the risk of being killed, the sound is a cue for the predator about the location of its prey. When an alert animal deliberately gives a warning call to a stalking predator resulting in the predator giving up the hunt, this sound, the alert call, is a signal both for conspecifics and the predator. Different species can, thus, communicate by means of signals which both recognize and behave accordingly.
Secondary sexual traits are features that distinguish the two sexes of a species, but that are not directly part of the reproductive system. They are probably the product of sexual selection for traits, which give an individual an advantage over its rivals in courtship and competitive interactions. Secondary sexual traits are also cues for the opposite sex. They are not directly related to a better production of offspring, but are normally good indicators of better sperm quality or egg production, e,g, manes of male lions (Panthera leo) and long feathers of male peacocks (Pavo cristatus). In humans, visible secondary sexual traits include enlarged breasts of females and facial hair on males.
The study of signals and cues is more complex that it may appear at first sight. Cues can become signals. In 1952, Niko Tinbergen described ritualization as the evolutionary process whereby a cue may be converted into a signal, e.g. the canine behavior of baring teeth. In 1975, Zahavi described the handicap principle where the reliability of some signals is ensured because they advertise greater costs than absolutely necessary, e.g. the exaggerated plumage of the peacock.
We must understand correctly what the intentionality of signals means and not to confound the intentionality of the signal itself with its origin, development and evolution. Signals do not origin by design with a determined purpose. Some features or behaviors just happen at a certain time to be efficient for an organism in generating in another organisms the right behavior at the right time. If they convey an advantage to these organisms in their struggle for survival (and reproduction), they will spread in the population (provided these organisms reproduce). With time, they gain intentionality and become true signals, but their origin was accidental like everything else. This is the reason why I had to modify (some extensively) the definitions I use in this text and I had to create new ones—to make them compatible with the Darwinian theory of evolution.
Applying the principle of simplicity, as always, I suggest the following definitions:
A signal is everything that intentionally changes or maintains the behavior of the receiver. A cue is everything that unintentionally changes or maintains the behavior of the receiver (see “The 20 Principles All Animal Trainers Must Know“).
These definitions open for the possibility to better distinguish between the intentional signals (proper signals) we send and the unintentional ones (which are cues). For example, many dog owners say “no” to their dogs meaning “stop what you are doing,” but their (unintentional) body language (cue) says “yes.”
In conclusion: signal is the most correct term to denominate what we use when we communicate with our animals; and signals may assume many forms, auditory (the words we use), visual (the hand movements and body language we use), olfactory (in canine detection work), tactile (a touch, very common in horse training) and probably also palatable.
So, enjoy the consequence of your (intentional) signals and be careful with any cues you may be (inadvertently) sending to your favorite animal. Enjoy as well your further studies of this fascinating topic: animal communication.
References and further readings
- Dawkins, M. S., and T. Guilford (1991). The corruption of honest signalling. Animal Behaviour 41:865–873.
- Donath, J. (2007). Signals, cues and meaning (February draft for Signals, Truth and Design. MIT Press)
- Hasson, Oren (1997). Towards a general theory of biological signaling. Journal of Theoretical Biology 185: 139-156.
- Hauser, Marc D. and Mark Konishi, eds. (1999). The design of animal communication. Cambridge: Bradford/MIT Press.
- Maynard Smith, John and David Harper (1995). Animal signals: Models and terminology. Journal of Theoretical Biology 177: 305-311.
- Maynard Smith, John and David Harper (2003). Animal signals. Oxford University Press, UK.
- McFarland, D. (1999). Animal Behaviour. Pearson Education Limited, UK.
- Otte, D. (1974). Effects and functions in the evolution of signaling systems. Annual Review of Ecology and Systemat- ics 5:385–417.
- Saleh, N et al. (2007) Distinguishing signals and cues: bumblebees use general footprints to generate adaptive behaviour at flowers and nest. Arthropod-Plant Interactions, 2007, 1:119–127
- Schaefer, H. M. and Braun, J. (2009). Reliable cues and signals of fruit quality are contingent on the habitat in black elder (Sambucus nigra). Ecology, 90(6), 2009, pp. 1564–1573.
- Searcy, W. A., and S. Nowicki (2005). The evolution of animal communication. Princeton University Press, Princeton, New Jersey, USA.
- Tinbergen, N. (1952). The curious behavior of the stickleback. Scientific American December 1952.
- Zahavi, A. (1975). Mate selection: a selection for a handicap. Journal of Theoretical Biology 53:204–214.
Featured image: Secondary sexual traits, as the mane of the male lion, are powerful cues (Photo by Luca Galuzzi via Wikipedia).
Featured Course of the Week
Ethology Ethology studies animal behavior in its natural environment. It is one of the fundamental courses in your curriculum. A reliable knowledge of animal behavior is the basis to create a satisfying relationship with any animal we train.
Featured Price: € 168.00 € 98.00

Learn more in our course Animal Learning. This online course explains how animals acquire the various behaviors they display— which is essential knowledge for you to learn how to train and modify the behavior of your companion animal. This course teaches you also how to create reliable and successful training plans. Roger Abrantes (Ph.D. in Evolutionary Biology and Ethology) wrote the included textbook as a beautiful flip page book.